
Development of socially interactive and emotionally sensitive artificial intelligence systems using big and thick behavioral and neuroimaging data
Principal Investigator | Tsung-Ren Huang, assistant professor Department of Psychology, NTU
Co-Principal Investigator |
Jyh-Horng Chen, Professor EE Dept, NTU
Li-Min Wang, Professor Physics Dept, NTU
Hsueh-Chih Chen, Professor EPC Dept, NTNU
Principal Investigator | Tsung-Ren Huang, assistant professor Department of Psychology, NTU
Co-Principal Investigator |
Jyh-Horng Chen, Professor EE Dept, NTU
Li-Min Wang, Professor Physics Dept, NTU
Hsueh-Chih Chen, Professor EPC Dept, NTNU
Project Intro
A better understanding of how the human brain and mind work can help us design better artificial intelligence (AI) systems and robots, and better AI systems and robots can be applied in research to help gain a better understanding of how the human brain and mind work. For this purpose, the team of the NTU neuroimaging center collaborates with scholars and experts from NTNU to: (1) understand how the brain process social and emotional information using machine/deep learning techniques, and (2) develop a socially interactive and emotionally sensitive chatbot. Specifically, the subproject 1 “fMRI hyperscanning for social interaction research”will build a system to synchronize the three MRI scanners in NTU, NCCU, & NCKU for studying the brain activities during social interaction; the subproject 2 “Investigating embodiment of emotion and cognition using MEG”will use MEG to clarify how bodily states and environmental factors affect cognitive and emotional states in the brain; the subproject 3 “A data sharing and analytics platform for the Imaging Center for Integrated Body, Mind, and Culture Research”will integrate data of the same research participant from different studies to accumulate big and deep/thick data in the neural and behavioral domains; the subproject 4 “Developing a sympathetic and humorous chatbot”will construct a chatbot in Mandawhrin Chinese, which will then be validated by the subprojects 1 & 2 for its humanness in social interaction and effectiveness in reducing human anxity/depression.
A better understanding of how the human brain and mind work can help us design better artificial intelligence (AI) systems and robots, and better AI systems and robots can be applied in research to help gain a better understanding of how the human brain and mind work. For this purpose, the team of the NTU neuroimaging center collaborates with scholars and experts from NTNU to: (1) understand how the brain process social and emotional information using machine/deep learning techniques, and (2) develop a socially interactive and emotionally sensitive chatbot. Specifically, the subproject 1 “fMRI hyperscanning for social interaction research”will build a system to synchronize the three MRI scanners in NTU, NCCU, & NCKU for studying the brain activities during social interaction; the subproject 2 “Investigating embodiment of emotion and cognition using MEG”will use MEG to clarify how bodily states and environmental factors affect cognitive and emotional states in the brain; the subproject 3 “A data sharing and analytics platform for the Imaging Center for Integrated Body, Mind, and Culture Research”will integrate data of the same research participant from different studies to accumulate big and deep/thick data in the neural and behavioral domains; the subproject 4 “Developing a sympathetic and humorous chatbot”will construct a chatbot in Mandawhrin Chinese, which will then be validated by the subprojects 1 & 2 for its humanness in social interaction and effectiveness in reducing human anxity/depression.
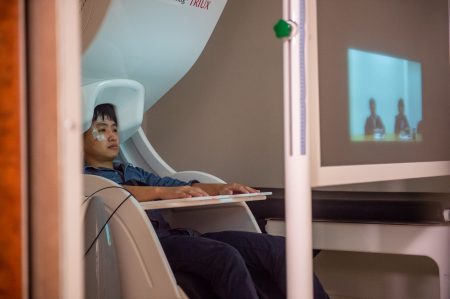
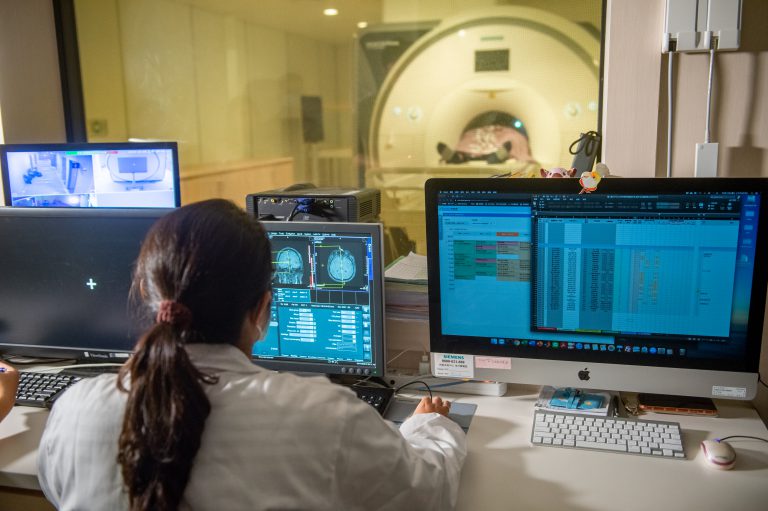
Product Features
- Able to objectively evaluate the effectiveness of various AI dialogue systems by examining the process of human-computer interaction, such as: (1) Grammatical errors; (2) Unclear semantics and words without meaning; (3) No interactive ground to consider; (4) Whether the response triggers positive or negative emotions of the user.
- The developed empathy dialogue module can be embedded in various forms of dialogue systems, such as Line chat rooms, Telegram chat groups, Zenbo robots, etc. Therefore, it is possible to have one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-one chats with users through text or voice.
Market for our Product / Technologies
- Online Emotional Support Chat System
- Entertainment or Healthcare Companion Robot
- Voice or Text Customer Service Robot
Contact info
Tel :02-3366-3104
Mail:trhuang@g.ntu.edu.tw
Tel :02-3366-3104
Mail:trhuang@g.ntu.edu.tw
